- Green Infrastructure
To be smart and sustainable university by 2030, which related to SDG 3, SDG 9, SDG 11, and SDG 17, by elaborating master plan and sustainable university policies
KMUTT has been recognized as the outstanding university in Thailand. KMUTT is not only content to just be one of Thailand’s leading engineering universities, but also aiming to have its impact felt globally. KMUTT has developed the Global Player Strategy, aimed at producing graduates who excel at communication and leadership as well as having outstanding technical skills. Through a combination of hard work and passion for learning and discovery, KMUTT has also offered our excellences in both teaching and research to educate and encourage our students and staff forwards to be a Green University. KMUTT has responsibility to contribute our knowledge to conduct a role model on energy, environment safety management systems, which can promote the development of sustainability on our campuses and finally expand to our societies for a better quality of life. The university is committed to be a leader in sustainable development, in all activities from operations, teaching and research.
CAMPUSES & SITES
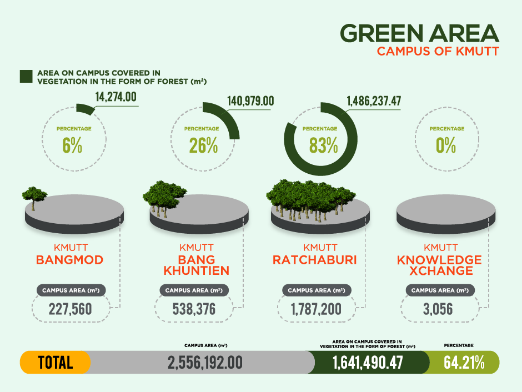
KMUTT has 4 campuses /sites which have the total area of 2,556,192.00 sq. meters including:
+ KMUTT Bangmod Campus 227,560 sq. meters
+ KMUTT Bang Khun Thian Campus 538,376.00 sq. meters
+ KMUTT Ratchaburi Learning Park 1,787.200 sq. meters
+ KMUTT KX 3,056.00 sq. meters
- Energy and Climate Change
To meet the energy and climate challenge by 2024 which are related to SDG 7, SDG 13, and SDG 15, we actively work on energy reduction, implementation of energy efficient appliances, renewable energy usage, climate change and green area expansion
Energy and climate change at KMUTT focus on the activities which comply to SDG 2030 Goal 7-Affordable and clean energy and Goal 13-Climate action to ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable, and modern energy. KMUTT concerns to the use of energy and climate change issues and provide the energy reduction policy, renewable energy usage policy and greenhouse gas emission reduction policy including the energy efficient appliances usage, the implementation of smart buildings/green buildings, total electricity use, energy conservation programs, climate change adaptation and mitigation programs. Moreover, KMUTT has our plan to facilitate access to clean energy research and technology, including renewable energy, energy efficiency and advanced and cleaner fossil-fuel technology, and promote investment in energy infrastructure and clean energy technology.
- Waste
To be a pilot model on both municipal and hazardous waste management system, which related to SDG 3, SDG 11, SDG 12 and SDG14
Waste management play a key role in SDG 2030 Agenda, especially in the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) for sustainable cities and communities (SDG 11), for responsible consumption and production (SDG 12) and for life below water (SDG 14):
SDG 11.6: By 2030, reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities, including by paying special attention to air quality and municipal and other waste management.
SDG 12.4: By 2020, achieve the environmentally sound management of chemicals and all wastes throughout their life cycle, in accordance with agreed international frameworks, and significantly reduce their release to air, water and soil in order to minimise their adverse impacts on human health and the environment.
SDG 12.5: By 2030, substantially reduce waste generation through prevention, reduction, recycling and reuse.
SDG 14.1: By 2025, prevent and significantly reduce marine pollution of all kinds, in particular from land-based activities, including marine debris and nutrient pollution.
Developing fully-functional waste management systems and a circular economy contributes positively to achieving other goals, too, for example those for health (SDG 3), decent work (SDG 8) and climate action (SDG 13).
WASTE
Waste is one of environmental problems of national concern according to the lack of improper management. KMUTT is one of educational institute who has a significant environmental impact including hazardous waste and municipal solid waste and try to reduce these impacts with possible save the university resources and money. The waste in KMUTT has been concerned on Hazardous waste, Municipal solid waste, and Wastewater.
HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
Hazardous Waste in KMUTT mostly came from laboratory waste. Laboratory operations for education and research are the primary hazardous waste-generating activities within KMUTT. The improper disposal of the hazardous waste is a problem of national concern that pollutes the environment and harms to living organisms including human beings. Hazardous waste management has been set up within KMUTT and aim to play an important role to maintain a safe and environmentally responsible within the university.
MUNICIPAL SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
Municipal solid waste is a serious problem facing in all areas of Thailand including educational institute. The increasing of municipal solid waste generation each year leads to environmental problems. KMUTT is one of educational institute who has a significant environmental impact including municipal solid waste and try to reduce this impacts Proper management of hazardous waste and municipal solid waste will minimize the risk to students, employees, and members of the public and possible save the university resources and money.
WASTEWATER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
Wastewater quality from research buildings, study buildings and natural ponds have to follow the sewerage disposal regulations to monitor the water quality by monthly check up and treatment before disposal to domestic water pipe which send to BMA Domestic Waste Treatment Plant near the university. To monitoring water quality, the effluent from onsite wastewater treatment plant in each building had been analyzed monthly by student teams.
- Water
To be university with clean water and sanitation by 2030, which related to SDG 6, by elaborating good water conservation program
WATER AND SDG 2030
+ Too many people still lack access to safely managed water supplies and sanitation facilities. Water scarcity, flooding and lack of proper wastewater management also hinder social and economic development. Increasing water efficiency and improving water management are critical to balancing the competing and growing water demands from various sectors and users. In 2017–2018, 157 countries reported average implementation of integrated water resources management of 48 per cent.
+ Based on data from 62 out of 153 countries sharing transboundary waters, the average percentage of national transboundary basins covered by an operational arrangement was only 59 per cent in 2017.
Source: Report of the Secretary-General, The Sustainable Development Goals Report 2018
KMUTT WATER CONSERVATION POLICY
- Work with our communities to develop awareness of “why” and “how” we should reduce our water consumption.
- Reduce pipe water usage 30 % by 2030 compared to the 2006 baseline.
- Increase Rainwater / Natural Water Resource usage 20 % by 2020.
- Implement water recycling program for sanitary and water usage 25% in new buildings since 2003 compared to 2018.
- Achieve safe drinking water and clean wastewater in campus-wide by 2023.
- Transportation
Being a walk and bike society is related to SDG 3, SDG 7, and SDG 13 by sustainable mobility implementation for all in KMUTT by 2024
Although sustainable transport is not represented by a standalone SDG in the 2030 Agenda, it is mainstreamed in a direct or indirect manner into many of the proposed SDGs, especially those related to food security, health, energy, infrastructure, cities and human settlements, and climate change. Transport services and infrastructure are essential to achieving most, if not all, SDGs:
Transport-Relevant SDG Targets
The 2030 Agenda states that sustainable transport systems, along with universal access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy services, quality and resilient infrastructure, and other policies that increase productive capacities, would build strong economic foundations for all countries. The text includes five targets that are directly related to the transport sector and seven other targets that are indirectly related to the transport sector.
Transport contributes directly to five targets on road safety (Target 3.6); energy efficiency (Target 7.3); sustainable infrastructure (Target 9.1), urban access (Target 11.2), and fossil fuel subsidies (Target 12.c) emphasize that sustainable transport is not needed solely for its own sake, but rather is essential to facilitate the achievement of a wide variety of SDGs.
Transport also contributes indirectly to seven SDG targets on agricultural productivity (Target 2.3), air pollution (Target 3.9), access to safe drinking water (Target 6.1), sustainable cities (Target 11.6), reduction of food loss (Target 12.3), climate change adaptation (Target 13.1), and climate change mitigation (Target 13.2).
Sources: http://www.slocat.net/sdgs-transport
KMUTT transportation policy has been launched since 2010 and run one of the most comprehensive programs to reduce university-related traffic impacts—it’s an essential part of our drive for sustainability. Transportation, accounts for 5 percent of KMUTT’s greenhouse gas emissions. Increasing the use of alternative transportation reduces those emissions and makes our community a better place to live and work. KMUTT focus on limitation of car usage & carpool promotion, Walk & Bike society and Clean Energy usage for university van& bus. The transportation policy have been implemented within our university since 2011.And now, we are ready to expand our system and policy to surround communities and make sustainability for all in KMUTT.
Energy Environmental Safety and Health (EESH) and Sustainable office of KMUTT set new bar in terms of how university can be more responsible to the environment by using “Green Society building” under the concept of ‘Walk and Bike Society’. This building is the bike service center where student and staff could either borrow bicycle or repair their bike. The partnership between EESH and Sustainable office of KMUTT together with student will lead to developing sustainable products together.
- Health and Safety
Health and safety activity for all in KMUTT by the year 2030, which related to SDG 3, SDG11, SDG 12
KMUTT: SAFETY AND SDG 2030
Safety is one of a key role for sustainability which related to health. Road safety targets have been included in the final text of the new Sustainable Development Goals adopted by UN member states in New York. A specific stand-alone target in the Health Goal to reduce road traffic fatalities by 50% by 2020 and a target on sustainable urban transport in the Cities Goal have been approved, in a landmark achievement for the global road safety community. The SDGs designed to ‘stimulate action in areas of critical importance for humanity and the planet’. The final wording of the targets, which will be formally adopted by world leaders at a special summit in New York is:
Goal 3:
Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages:
3.6. By 2020, halve the number of global deaths and injuries from road traffic accidents (In the Health Goal, the stand-alone road safety target is lined up alongside other major priorities including maternal and under-5 mortality, AIDS and universal health coverage. The 2020 SDG target is far more ambitious than the 2020 goal set for the UN Decade of Action for Road Safety to ‘stabilize and reduce’ road deaths.)
Goal 11:
Make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable: 11.2. By 2030, provide access to safe, affordable, accessible, and sustainable transport systems for all, improving road safety, notably by expanding public transport, with special attention to the needs of those in vulnerable situations, women, children, persons with disabilities and older persons. On safety issues the relevant SDG Targets related to Health and Safety at the Workplace concerned on SDG Goal 3, Goal 8, and Goal 16
Goal3:
3.9 By 2030 substantially reduce the number of deaths and illnesses from hazardous chemicals and air, water, and soil pollution and contamination 3.a strengthen implementation of the Framework Convention on Tobacco Control in all countries as appropriate
Goal8:
8.8 Protect labor rights and promote safe and secure working environments of all workers, including migrant workers, particularly women migrants, and those in precarious employment
Goal16:
16.6 Develop effective, accountable and transparent institutions at all levels